
Ø
GDP (Gross domestic product)
- The final products within the boundaries of India within that specific period of time are in the GDP of India. Further, the effect of inflation on these products is also calculated.
- GDP includes government expenditures, consumption, exports, imports, and investment of India.
- For example, if Honda decides to manufacture it’s parted in India than that will go into the GDP of India. But the revenues got through the sales are included in the GDP of Japan.
Ø
GNP (Gross national product
- GNP of the country is measured by the income which is collected due to the various factors of production that are owned by the residents or the citizens of India. The GNP of India is calculated by adding the net inflow coming from the abroad countries to the GDP of India while subtracting net outflow to the foreign countries from India.
As per the
previous example, if Honda is an Indian company and it is selling its parted in
other countries than that revenue becomes the GNP for India.
Ø
NET DOMESTIC PRODUCT (NDP)
The net domestic product (NDP) equals the gross domestic product (GDP) minus depreciation on a country's capital goods. Net domestic product accounts for capital that has been consumed over the year in the form of housing, vehicle, or machinery deterioration.
Ø Net National Product (NNP)
"Net national Product or
national income at
market prices is the net market money value of all the final goods and services
produced in a country during a year. It is found out by subtracting the amount
of depreciation of the existing capital in a year from the market value of all
final goods and services".
For a continuous flow of money payments, it is
necessary that a certain amount of money should be set aside from the gross
national income for meeting the necessary expenditure of wear and tear of all
capital equipment so that there should not be any deterioration in the capital
and it should remain intact. If we deduct depreciation allowance from gross
national product, we get Net National Product at current market price.
Formula for
Net National Product/National Income:
NNP
at Market Price = GNP at Market Price - Depreciation
PER CAPITA INCOME (PCI)
PER CAPITA INCOME (PCI)
It measures
the average income earned per person in a given area (city,
region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the
area's total income by its total population.
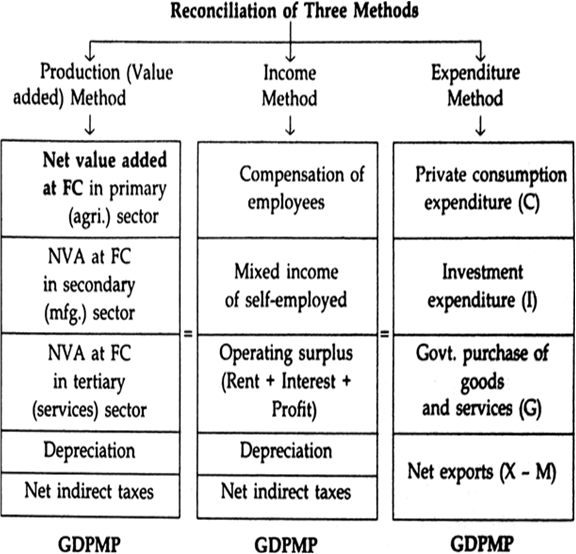
MEASURING NATIONAL INCOME
- Product/Production Method: It refers to the addition of value to the raw material (intermediate goods) by a firm due to its production activities.
- It is also known as ‘Inventory method’ or ‘Commodity Service Method’. It consists in finding out the market value of all goods and services produced in a country during a given period.
- We sum up the value of the gross product of all producers in an industry and from this total are deducted the value of the intermediate products consumed and depreciation of equipment during the process of production.
* Value added = Value of output – Intermediate consumption.
Q. What are the steps involved in
value added method?
Ø Classify all the
production units located in the domestic territory into distinct industrial
sectors: The units are classified into primary, secondary and tertiary sectors
which are further classified into sub-sectors like agriculture, manufacturing,
banking, etc.
Ø Estimate NVAFC of
each industrial sectors by taking the following sub-steps:
1.Estimate the value of
output and it can be estimated in two ways, firstly sum of sales and net
addition stock.
2.Deduct intermediate
consumption from value of output to arrive at GVAMP.
3.Deduct consumption of
fixed capital from GVAMP to arrive at NVAMP.
4.Deduct net indirect tax
from NVAMP to arrive at NVAFC of an industrial sector.
- Take the sum of NVAFC of all the industrial sectors of the economy. By doing so, we will arrive at net domestic product at factor cost (NDPFC).
- Add net factor income from abroad to NDPFC arrive at national income.
Q. Explain
the problem of double counting?
The term double counting
refers to an output more than once while passing through various stages of
production. It leads to over-estimation of national income or domestic income
in the economy. It can be explained with the help of an example:
- Stage1: Suppose a farmer produces 50kg wheat and sells is at Rs.5000 to the miller (flour mill). Therefore, final value of wheat for the farmer is Rs.5000.
- Stage2: For miller, whet is an intermediate good. He converts it into flour and it for Rs.700 to a baker. Therefore, final value of the flour for the miller will be Rs.700.
- Stage3: For baker, flour is an intermediate good. He manufactures bread from it and sells the bread to the final consumers for Rs.1000. Therefore, final value of bread for the baker is Rs.1000.
- If adding all the values of final goods (output), the total value of output = 500 + 700 + 1000 = Rs.2200.
Q. How is
the ways of avoiding double counting avoided?
The two alternative ways of avoiding double counting:
- Take value added instead of total output: It is necessary to identify intermediate consumption for this. From the above example, the intermediate consumption of farmer is nil. Whereas, that of baker and grocer is Rs.1000 and Rs.2000 respectively.
Thus, the sum total of
value added by farmer, baker and grocer is Rs.2200. Therefore, this is the
value that should be added in the national income as it is free from double
counting.
- Take the value of only the final product (output): The final products are those products which are purchased for consumption and investment. In the above example, only the value of grocer i.e. Rs.2200, is the final product because only he sells the entire output to the consumers.
- This value i.e. Rs.2200 includes the value added by all the three levels of production unit taken together which are Rs.1000 of farmer, Rs.1000 of baker and Rs.200 of the grocer.
Production
unit
Value
of output – Intermediate consumption.
Value
added
Farmer
500 – 0
500
Miller
700 – 500
200
Baker
1000 – 700
300
Total
2200 – 1200
1000
Q.
Explain how income generated in the economy is equal to NVAFC or
domestic income?
Or
Production
unit
|
Value
of output – Intermediate consumption.
|
Value
added
|
Farmer
|
500 – 0
|
500
|
Miller
|
700 – 500
|
200
|
Baker
|
1000 – 700
|
300
|
Total
|
2200 – 1200
|
1000
|
Q.
Explain how income generated in the economy is equal to NVAFC or
domestic income?
2.
The
Income Method:
This method consists in adding together all the income that accrued to the factors of production by way of wages, rents, interests and profits. This gives us national income classified by distributive shares. The factor owners are paid for the productive services rendered by them in money. The total money payments made to the factors of production in the economy represent the total money value at factor cost. What is factor payment (cost) for the producers is factor income (earning) for the factor owners. Thus, under income approach GNP is found by adding up the total factor incomes generated in producing the national product.
Components
of Income Method:
Ø Compensation of employees: It refers to the amount paid to
employees by employer for rendering productive services.
a) Wages and salaries in cash: It includes all monetary benefits
like wages, salaries, bonus, commission, etc.
b) Wages and salaries in kind: It includes all non-monetary
benefits like rent, free home, free car, free transport, imputed interest of
interest free loans, etc.
c) Employer’s contribution to social security schemes: It includes contribution
made by the employer for the social security of employees such as contribution
to provident funds, gratuity, retirement pension, insurance, etc.
Ø Rent and Royalty: Rent is that part of national income
which arises from ownership of land and building. Royalty refers to income received from granting leasing rights of
sub-soil assets.
Ø Interest: It refers to amount received from lending funds to a
production unit.
Ø Profit: It is the reward to the entrepreneur for his contributions to
the production of goods and services. It includes:
a) Corporate tax: It is direct tax paid by an enterprise to the
government on the total profit earned by it.
b) Dividend: It refers to that part of profit which is paid to the
shareholders in the ratio of their shareholding.
c) Retained earnings: It refers to that part of profit
which is kept as reserve to meet unexpected contingencies or business
expansion.
d) Mixed Income: It is the income of the unorganized sector or the
self-employed people. In this sector factors of production are not hired from
factor market. Rather, own resources are used in the production. So the income
generated in this sector will be mixture of rent, interest, profit and wages
and they cannot be separated from each other. That’s why, it is called mixed
income of self-employed.
For e.g.: Doctor running his
own clinic, CA practicing from his house, etc.
Q.
What are the steps of income method in estimating national income?
3. The Expenditure Method:
Under this
method we add up personal consumption expenditures, the gross private domestic
investment, the Government purchase of goods and services and the net foreign
investment to obtain GNP at market prices. We deduct depreciation to obtain Net National Product (NNP) at market price, less Indirect Taxes give us net national income at factor
cost. In this method of national product measurement, the GNP is regarded as a
flow of total goods and services bought through the money payments by the
community.
Components of Expenditure Method:
Ø Private
Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE): It refers to expenditure incurred by the
households and private non-profit institutions serving households of all types
of consumer goods i.e. durable goods, non-durable goods, semi-durable goods and
services.
Ø Government
Final Consumption Expenditure (GFCE): It refers to the expenditure incurred by
general government on various administrative services like law and orders,
defense, education, etc.
Ø Gross
Domestic Capital Formation (GDCF)/Gross Investment: It refers to the addition to capital stock of
the economy.
Ø Net Exports
(X - M): It refers to
the difference between export and imports of a country during a period of one
year.
Q. What are the steps of expenditure method in
calculation of national income?
The steps of expenditure method in calculation of national income are as follows:
Step1: Identify the economic units incurring final expenditure. These economic units are classified into four groups:
NDPFC = GDPMP – Depreciation – Net Indirect taxes.
Step4: Estimate net factor income from abroad (NFIA) to arrive at national income. NFIA is added to domestic income to get National income.
NNPFC = NDPFC + NFIA.
The steps of expenditure method in calculation of national income are as follows:
Step1: Identify the economic units incurring final expenditure. These economic units are classified into four groups:
a) Households
b) Government
c) Production unit
d) Rest of the world.
Step2: Classification of final expenditure. The above
economic units estimated as:
a) Private final consumption expenditure (PFCE)
b) Government final consumption expenditure (GFCE)
c) Gross domestic capital formation (GDCF)
d) X – M (export - import).
The sum total of these four component gives
GDPMP.
Step3: Calculate domestic income (NDPFC).
By subtracting the amount of depreciation and net indirect taxes from GDPMP,
we get domestic income.NDPFC = GDPMP – Depreciation – Net Indirect taxes.
Step4: Estimate net factor income from abroad (NFIA) to arrive at national income. NFIA is added to domestic income to get National income.
NNPFC = NDPFC + NFIA.
Nic
ReplyDeleteVery informative article! Keep sharing.
ReplyDeleteNice 👌
ReplyDeleteNice👌
ReplyDelete